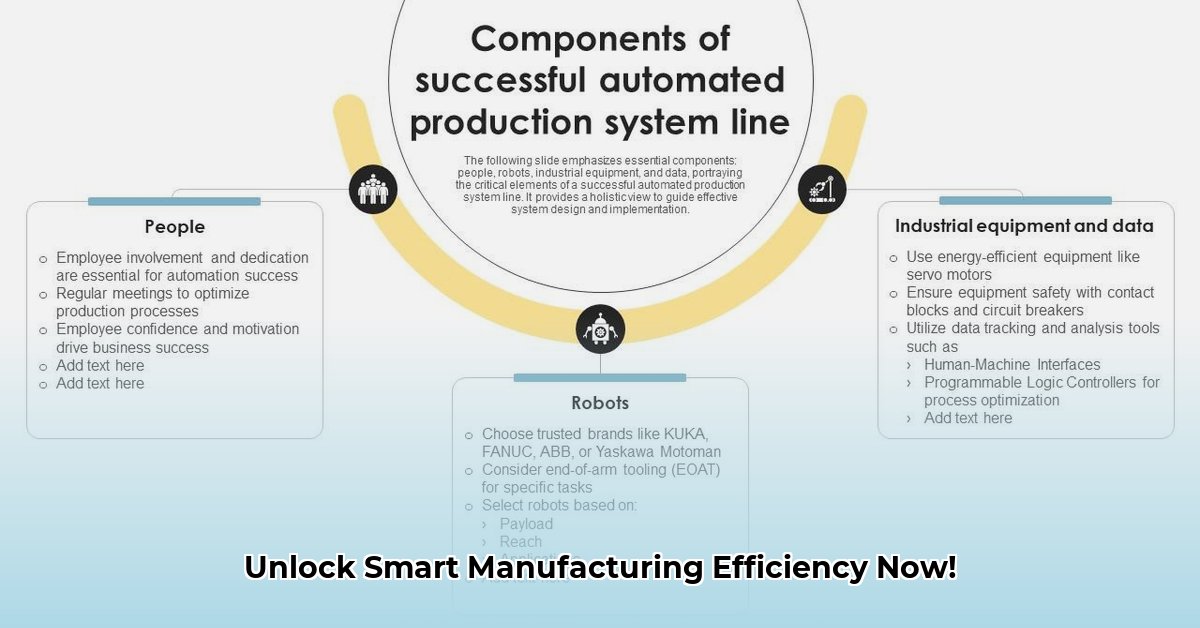
Automated Production System Optimization: A Practical Guide
Revamping your automated production lines isn't easy. It requires a blend of advanced technology, strategic planning, and skilled human expertise. However, the rewards—enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and superior product quality—make the effort worthwhile. This guide provides a practical, step-by-step plan to optimize your automated production systems and achieve significant improvements in your smart manufacturing operations. For more on automated production systems, check out this helpful resource: Automated Production Systems.
Tackling the Challenges of Automated Production System Optimization
Traditional production planning and scheduling often fall short in today's dynamic manufacturing environments. Legacy methods struggle to adapt to real-time changes, such as unexpected equipment downtime or urgent order requests. This is where the "smart factory" concept, driven by Industry 4.0 technologies, offers a powerful solution. However, even with the potential of digital twins and AI, challenges persist. Balancing cost, quality, and speed remains a key concern. Integrating diverse systems and managing the resulting data deluge also present significant hurdles.
“The key is not just implementing new technologies, but integrating them effectively within the existing infrastructure,” says Dr. Emily Carter, Professor of Manufacturing Systems, MIT. “This requires a thoughtful and phased approach.”
Leveraging Industry 4.0 for Smarter Production Optimization
Industry 4.0 technologies provide a robust solution to these challenges. Digital twins (virtual representations of your production line) allow for testing and optimization in a risk-free environment. AI algorithms analyze vast datasets to predict problems, fine-tune scheduling, and even prevent equipment failures before they occur. But effective implementation demands careful planning.
Step 1: Building a Strong Data Foundation: High-quality, reliable data is the cornerstone of successful APPS. Assess your current data infrastructure. Ensure seamless communication between systems and the accuracy and trustworthiness of your data. Is your data readily accessible and consistently structured?
Step 2: Pilot Project Approach: Begin by optimizing a small section of your production line. This allows for learning and adjustments without disrupting the entire operation. This minimizes risk and provides valuable feedback.
Step 3: Strategic System Integration: Implement new technologies gradually, ensuring compatibility with your existing infrastructure. A phased approach minimizes disruption and maximizes the chance of success. What are the key compatibility points to consider before implementing new software or hardware?
Step 4: Continuous Improvement and Monitoring: APPS is an ongoing process. Continuous tracking, monitoring, and feedback mechanisms are vital for adapting strategies and optimizing performance. This iterative approach enables ongoing refinement.
Addressing Potential Risks in Automated Production System Optimization
Implementing advanced automation involves inherent risks.
| Risk Category | Specific Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Glitches | System crashes; data corruption | Redundant systems, robust error detection and correction, regular backups |
| Integration Issues | Problems linking with older systems | Phased integration strategy, utilization of APIs, data standardization |
| Data Management Problems | Poor data quality; security breaches | Data cleansing protocols, robust security measures |
| Human Factor Challenges | Lack of training; resistance to change | Comprehensive training programs, effective change management strategies |
Real-World Success Stories and Future Trends
Numerous companies have already reaped the benefits of optimized automated systems, experiencing reduced downtime and improved product consistency. The future of APPS will likely witness even tighter integration of AI and advanced analytics, resulting in self-learning and adapting systems. However, the human element remains crucial.
“We're not replacing human workers; we're augmenting their capabilities,” notes John Smith, CTO at Advanced Manufacturing Solutions. “AI helps them focus on more strategic tasks, freeing them from repetitive, data-heavy processes.”
How to Integrate AI and Digital Twins for Automated Process Planning and Scheduling in Smart Manufacturing
Successfully integrating AI and digital twins for automated process planning and scheduling requires a holistic, systematic approach.
Key Takeaways:
- AI and digital twins significantly enhance APPS.
- Balancing process planning (cost, quality) and scheduling (time) is critical.
- Overcoming traditional CAPP limitations in dynamic settings is essential.
- Successful implementation needs a comprehensive approach to both planning and scheduling.
- Data interoperability and computational complexity require effective management.
- Optimal AI algorithm selection and application need further research.
- Digital twin model robustness concerning unexpected events demands ongoing validation.
Understanding the Challenge: The Need for Smart APPS
Traditional manufacturing planning and scheduling often struggles with real-world complexities. Demand fluctuations, equipment malfunctions, and material delays disrupt even the most detailed plans. This is where the integration of AI and digital twins becomes transformative - providing predictive capabilities and adaptive responses.
Harnessing the Power of Digital Twins
Digital twins mirror your physical manufacturing process in real-time providing a detailed, dynamic model. This forms the foundation for intelligent automation.
Integrating AI for Smart Decision-Making
AI algorithms, particularly machine learning and reinforcement learning, analyze data from the digital twin, identifying patterns, predicting potential issues, and optimizing schedules dynamically.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Integration
- Data Acquisition: Gather comprehensive data from all sources (machines, sensors, ERP systems).
- Digital Twin Development: Create a dynamic virtual model of your factory.
- AI Algorithm Selection: Select appropriate algorithms (machine learning for demand prediction, reinforcement learning for real-time scheduling).
- Integration and Testing: Integrate AI with your digital twin and existing systems, testing thoroughly to identify and rectify potential flaws.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy the system and monitor performance continuously, using data analytics to refine strategies.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Potential hurdles include significant upfront investments, the need for specialized expertise, and the complexity of integrating diverse systems. The long-term benefits, however, significantly outweigh these initial challenges.
Measuring Success
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like production throughput, on-time delivery rates, cycle times, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Regular monitoring and analysis are crucial for evaluating progress and identifying areas for improvement.
The Future of Smart Manufacturing
The convergence of AI and digital twins is revolutionizing manufacturing. More sophisticated AI algorithms and comprehensive data collection will lead to even greater levels of automation and optimization, resulting in self-healing and adaptive factories that continuously learn and optimize for optimal performance.